oxygen ion electrons|Electron Configuration for Oxygen (O, and O2– ion) : Tagatay Intro. How to find Protons & Electrons for the O 2- (Oxide ion) Wayne Breslyn. 754K subscribers. Join. Subscribed. 424. Save. 44K views 3 years ago. In this video we’ll use the Periodic table. How to convert Japanese yen to US dollars. 1 Input your amount. Simply type in the box how much you want to convert. 2 Choose your currencies. Click on the dropdown to select JPY in the first dropdown as the currency that you want to convert and USD in the second drop down as the currency you want to convert to.
PH0 · Oxygen Electron Configuration (O) with Orbital Diagram
PH1 · Oxygen
PH2 · O 2
PH3 · Naming monatomic ions and ionic compounds
PH4 · How to find Protons & Electrons for the O 2
PH5 · Electron configurations of ions (video)
PH6 · Electron Configuration for Oxygen (O, and O2– ion)
PH7 · Electron Configuration for Oxygen (O, and O2– ion)
PH8 · Chemistry of Oxygen (Z=8)
PH9 · 9.6: Electron Configurations of Ions
PH10 · 8.3: Electron Configurations
PH11 · 3.5: Formation of Ions and Ionic Compounds
Finde Optionen für Last-Minute-Flüge von Wien nach Zürich für spontane Reisen. Entdecke verfügbare Flüge und vergleiche Preise auf Basis der Suchen von Nutzer*innen. Sichere dir tolle Angebote für spontane Tripe .
oxygen ion electrons*******Intro. How to find Protons & Electrons for the O 2- (Oxide ion) Wayne Breslyn. 754K subscribers. Join. Subscribed. 424. Save. 44K views 3 years ago. In this video we’ll use the Periodic table.
135K views 4 years ago. In this video we will write the electron configuration for O 2-, the Oxide ion. We’ll also look at why Oxygen forms a 2- ion and how the electron configuration.Electron configuration The arrangements of electrons above the last (closed shell) noble gas. Melting point The temperature at which the solid–liquid phase change occurs. .Oxygen, for example, has the electron configuration 1 s2 2 s2 2 p4, whereas the oxygen anion has the electron configuration of the noble gas neon (Ne), 1 s2 2 s2 2 p6. The two .
Formation of Ions. In ordinary chemical reactions, the nucleus of each atom (and thus the element's identity) remains unchanged. Electrons, however, can be . The Origin and History. Oxygen is found in the group 16 elements and is considered a chalcogen. Named from the Greek oxys + genes, "acid-former", oxygen . The specific arrangement of electrons in orbitals of an atom determines many of the chemical properties of that atom. Orbital Energies and Atomic Structure. The energy of atomic orbitals increases as the . About. Transcript. To find the electron configuration for an ion, first identify the configuration for the neutral atom. Then, add or remove electrons depending on the .What kind of element is this ion, and what is its net charge? Show the answer. Ca. Charge from protons: 20 × ( 1 +) = 20 + Charge from electrons: 18 × ( 1 −) = 18 − Net charge: ( .
Because oxygen has a higher electronegativity than hydrogen, the shared electrons are closer to the oxygen atom than to the hydrogen atom. This is not the total transfer of electrons that would create an ion, but partial charges do form - the hydrogen end of the bond is partially positive (+1) because it has partially lost one electron, and .
Electrons and Electron Configuration. The number of electrons in an electrically-neutral atom is the same as the number of protons in the nucleus. Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Oxygen .with three unpaired electrons. The electron configuration of nitrogen is thus 1s 2 2s 2 2p 3. At oxygen, with Z = 8 and eight electrons, we have no choice. One electron must be paired with another in one of the 2p . Contributions & Attributions. 4.7: Ions- Losing and Gaining Electrons is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Atom may lose valence electrons quite to obtain a lower shell that contains an octet. Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge as a result because they are .
Oxygen is a chemical element; it has symbol . Because of its unpaired electrons, triplet oxygen reacts only slowly with most organic molecules, which have paired electron spins; this prevents spontaneous combustion. . Reactive oxygen species, such as . When forming ions, elements typically gain or lose the minimum number of electrons necessary to achieve a full octet. For example, fluorine has seven valence electrons, so it is most likely .

Electron configurations of ions. To find the electron configuration for an ion, first identify the configuration for the neutral atom. Then, add or remove electrons depending on the ion's charge. For example, to find the configuration for the lithium ion (Li⁺), start with neutral lithium (1s²2s¹). Then, since the lithium ion has one less . Generally, valence electrons can participate in the formation of chemical bonding, but core electrons cannot. While core electrons are not involved in bonding, they influence the chemical reactivity of an atom. The electron configuration of a oxygen atom is. O: 1s22s22p4 (1.9B.1) (1.9B.1) O: 1 s 2 2 s 2 2 p 4. which may be shorted.
Manish Bhardwaj. Bohr Diagrams of Atoms and Ions is shared under a CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by LibreTexts. Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun. In the Bohr model, electrons are pictured as traveling in circles at .
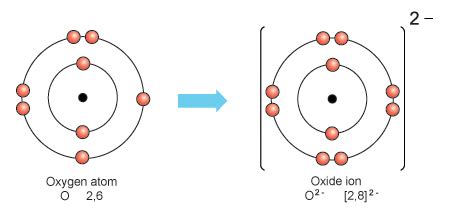
Above, it was easier for lithium to lose one electron than to gain 7 electrons. Similarly, it is easier for oxygen to gain 2 electrons instead of loosing 6 electrons: Oxygen Ion. The two gained electrons (purple dots) means that this oxygen ion has 10 electrons (-10 charge) and only 8 protons (+8 charge), giving the ion a net charge of -2.In chemistry, a superoxide is a compound that contains the superoxide ion, which has the chemical formula O − 2. The systematic name of the anion is dioxide(1−).The reactive oxygen ion superoxide is particularly important as the product of the one-electron reduction of dioxygen O 2, which occurs widely in nature. Molecular oxygen (dioxygen) .
These three electrons have unpaired spins. Oxygen (atomic number 8) has a pair of electrons in any one of the 2p orbitals (the electrons have opposite spins) and a single electron in each of the .
Contributions & Attributions. 4.7: Ions - Losing and Gaining Electrons is shared under a CK-12 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Marisa Alviar-Agnew & Henry Agnew. Atom may lose valence electrons to obtain a lower shell that contains an octet. Atoms that lose electrons acquire a positive charge as a result.
The charge on an ion is equal to the difference in the number of electrons and that of protons it contains- in other words, the number of electrons its parent atom has gained or lost. "O" + 2color(white)(l)e^(-) to "O"^(2-) An electrically-neutral oxygen atom gains two electrons to form an oxygen ion with two negative charges.oxygen ion electronsthe 3+ iron ion and the oxygen ion; Solution. To obtain a valence shell octet, sodium forms an ion with a 1+ charge, while the sulfur ion has a 2− charge. Two sodium 1+ ions are needed to balance the 2− charge on the sulfur ion. Rather than writing the formula as \(\ce{NaNaS}\), we shorten it by convention to \(\ce{Na2S}\). .oxygen ion electrons Electron Configuration for Oxygen (O, and O2– ion)the 3+ iron ion and the oxygen ion; Solution. To obtain a valence shell octet, sodium forms an ion with a 1+ charge, while the sulfur ion has a 2− charge. Two sodium 1+ ions are needed to balance the 2− charge on the sulfur ion. Rather than writing the formula as \(\ce{NaNaS}\), we shorten it by convention to \(\ce{Na2S}\). . 1 Answer. Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. To fill up the valence shell, which (when in oxygen's row) has 8 electrons, an oxygen atom wants to gain 2 electrons. Since every electron has a single negative charge, the addition of two electrons results in an oxygen ion with a charge of −2. This is true of every other element located beneath .Every subshell has a # of orbits s/p/d/f that can each hold 2 electrons each (one has the opposite spin of the other). The first shell (of all atoms) has 1 subshell of s-orbitals containing 1 s orbital. This means that the first shell can hold 2 electrons. The second shell has 2 subshells: 1 s-orbital and 3 p-orbitals.First Ionization Energy of Oxygen. First Ionization Energy of Oxygen is 13.6181 eV. Ionization energy, also called ionization potential, is the energy necessary to remove an electron from the neutral atom.. X + energy → X + + e −. where X is any atom or molecule capable of being ionized, X + is that atom or molecule with an electron removed .
For any help please contact [email protected] OK. Other Login Methods Login using EasyAuth. Tap the number shown below on the Authenticator app. Please ensure your device is connected to the internet. 60. Retry. Other Login Methods Login. Need Help? Proceed Need Help? Terms and Conditions .
oxygen ion electrons|Electron Configuration for Oxygen (O, and O2– ion)